
Your CFO can support various departments, ensuring your business has the financial insights and resources to function effectively. A CFO is instrumental in turning strategic visions into operational realities, working closely with other leaders to develop and implement growth strategies where finances are considered at every stage. Your CFO can ensure your business complies with financial regulations, tax laws, and reporting standards, avoiding costly penalties and legal issues.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
In many large enterprises, there are several key personnel who directly report to the CFO. Learn more about McKinsey’s Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice, and check out finance-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey. The lesson I learned was that if you treat everyone as your equal and care for them, then they are going to care a lot more about their jobs and be better at them.
A strategic partner in growth and scaling
Learn more as we guide you through the role, skills, and core responsibilities of a CFO. Liquidity refers to an organization’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities—those that will come due in less than a year—with readily accessible, or liquid, funds, namely cash and marketable securities. Liquidity is usually expressed as a ratio or a percentage of current assets to current liabilities. CFOs measure liquidity using several financial ratios, including current ratio and quick ratio.
Requirements and skills
While a CFO’s salary can vary based on industry, experience, and location, typical base salaries range from $84,000 to $239,000 a year. CFO stands for “chief financial officer.” The CFO is the top financial position held by an individual in a company or organization. Imagine if you could spot trends in customer sentiment and buying behavior across cfo title meaning your product portfolio in different geographies and use that data to more accurately forecast demand and financial performance. Modern financial systems use AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics to automate analysis. Even with extensive knowledge and experience in the field of finance, a CFO requires proper management skills.
- Others might get by with simply being aggressive and rubbing elbows with the right people.
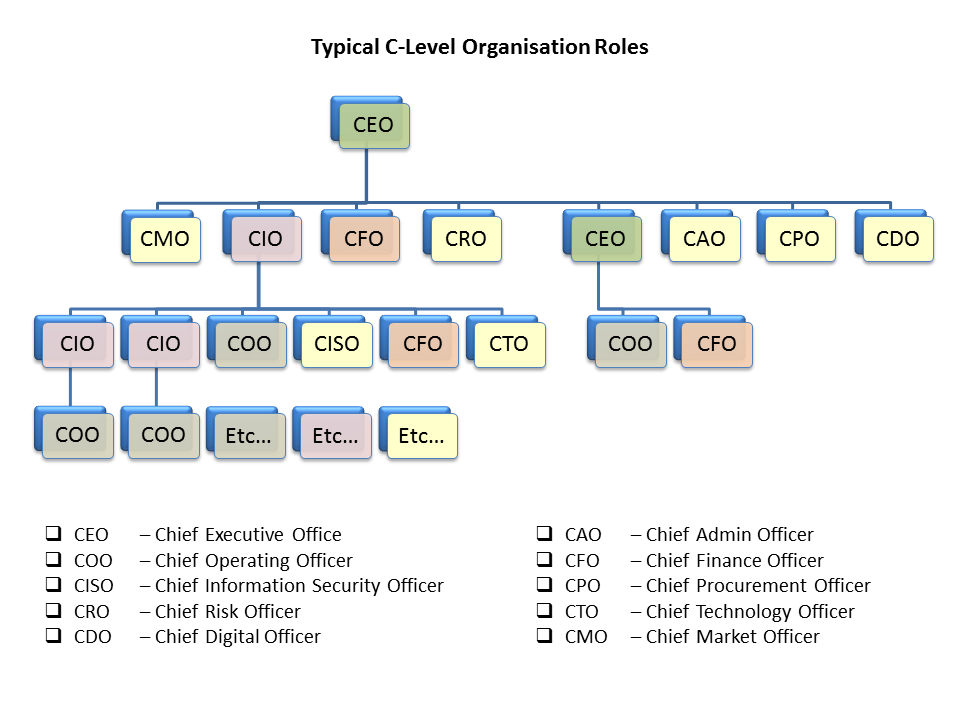
- And the Chief Technology Officer might report the Chief Information Officer.
- A chief risk officer is an executive whose role is to identify, analyze, and mitigate internal or external risks for an organization.
Early-stage companies might also engage a part-time or interim CFO for fundraising efforts and guidance. However, if you aspire to go public or need to satisfy fundraising or venture capital requirements, you will need more permanent help. However, the requirement for a CFO is often less about company size and more about having a strategic adviser with deep financial expertise on board. When your CFO collaborates with leaders of other business-critical areas, it’ll give you better insight into what’s driving your overall performance and where there’s room to improve. As small businesses grow, they encounter various risks, including market fluctuations, competition, and financial uncertainties. Your CFO will assess these risks and develop mitigation strategies to protect the business.
Changing role
The main responsibilities in the past were to reduce costs, optimize finance processes, and “keep score” by gathering data, running reports, and summarizing data. But CFOs now focus on supporting business model transformation—not just optimizing finance processes—but automating them. They report directly to the CEO and have a fiduciary responsibility to the Board of Directors and shareholders. CFOs are expected to be not only stewards of the finance department, but also strategic catalysts of company growth. The role has always been a central one to large public companies with multi-million revenues, but is becoming increasingly common in medium-sized and even small firms. Many start-ups, indeed, now hire a chief financial officer when they first start raising capital.
CFOs are generally equipped with advanced educational designations, such as a Master of Finance or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation. Many CFOs have professional backgrounds in fields such as accounting, investment banking, or financial analysis. For financial professionals, the CFO is among the most prestigious and highly paid positions available in a firm. People in this role have significant input in the company’s investments, capital structure, and how the company manages its income and expenses. This corporate officer may assist the CEO with forecasting, cost-benefit analysis, and obtaining funding for various initiatives.
Financial software systems must accommodate ongoing changes in the way financial accounting is regulated. Artificial intelligence is increasingly part of financial software; it can be especially helpful with forecasting and financial analysis. For that reason, along with being stewards and operators, today’s CFOs are strategists, helping to shape the company’s direction, according to Deloitte. They also are catalysts, cultivating a financial approach and mindset throughout the company to help other segments of the business perform better. The CFO is often considered the second highest-ranking person in a company after the CEO.
The company ended up making significant profits within two years of these changes. After I got my undergrad degree, my first job was as a statistical economist with the Bureau of Labor Statistics. I realized quickly that it wasn’t going to be a job that held my attention for very long. The information here will help you understand the duties, skills, and path to becoming a CFO.
